- acca article (pdf): http://www.accaglobal.com/content/dam/acca/global/PDF-students/2012s/sa_jan10_coulthurst.pdf
- Basic information, plus cvp analysis description: http://chandrasekharank.hubpages.com/hub/Decision-Making-Cost-Volume-Profit-Analysis
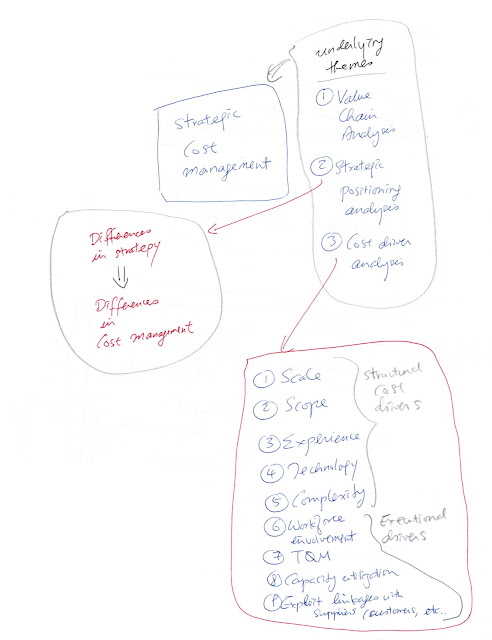
The topic is taught in Management Accounting; it often comes up in examination questions of Strategic Management Accounting.