A (brief) practice note on the construction of an academic literature review tree-b in the agile literature review approach (the academic-oriented project type):
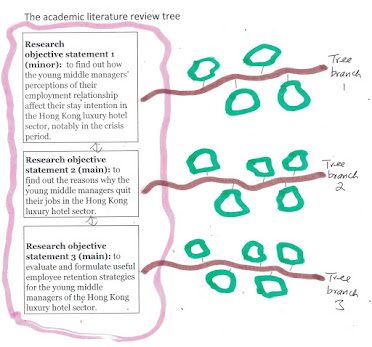
The discussion should start with an academic literature review tree, such as the following one (the example is from my previous blog note):
This tree has three tree root notes, each of which has a tree branch. Moreover, it can be said that:
Tree branch 1 belongs to SR (scientific reasoning) type and so does tree branch 2. Tree branch 3 is mainly a DT (design thinking) one. Both SR and DT types could involve some evaluation and exploratory investigation effort.
In order to construct an academic literature review tree-b, the researcher is going to map some research methods onto the academic literature review tree. The diagram of the academic literature review tree-b, roughly looks like the following one:
Regarding the academic literature review tree-b above, RM-1, RM-2, etc., are research methods, e.g., research interview, questionnaire survey and focus group, etc., that are mapped onto the academic literature review tree. Both primary and secondary research methods can be considered for research methods mapping. (note: if you are not sure what research methods to use for which research objective (as represented by the respective tree root node, do some literature review to learn what other researchers used to respond to a research objective similar to that of yours.)
The question now is what research method types are suitable for SR-type of research and what what research methods are suitable for DT-type of research?
I. Research methods to use for SR-type of tree branch:
a. Descriptive research: survey research, observations, case studies, among others.
b. Predictive research: quantitative research methods such as surveys, experiments, and statistical analysis are commonly used in predictive research.
c. Explanatory research (and causal research generally understood as the same explanatory research): in-depth interview, focus group, case studies, experiment, among others.
d. Exploratory research: focus group, survey research, unstructured interview research, among others.
e. Evaluation research: survey research, in-depth interviews, focus group, among others.
a. Design research: field observations, stakeholder interviews, feedback surveys, and focus group, among others.
b. Exploratory research: focus group, survey research, unstructured interview research, among others.
c. Evaluation research: survey research, in-depth interviews, focus group, among others.
Both primary and secondary research can be employed for SR-type and DT-type of research investigation.
Additional resource on research methods (videos).

No comments:
Post a Comment